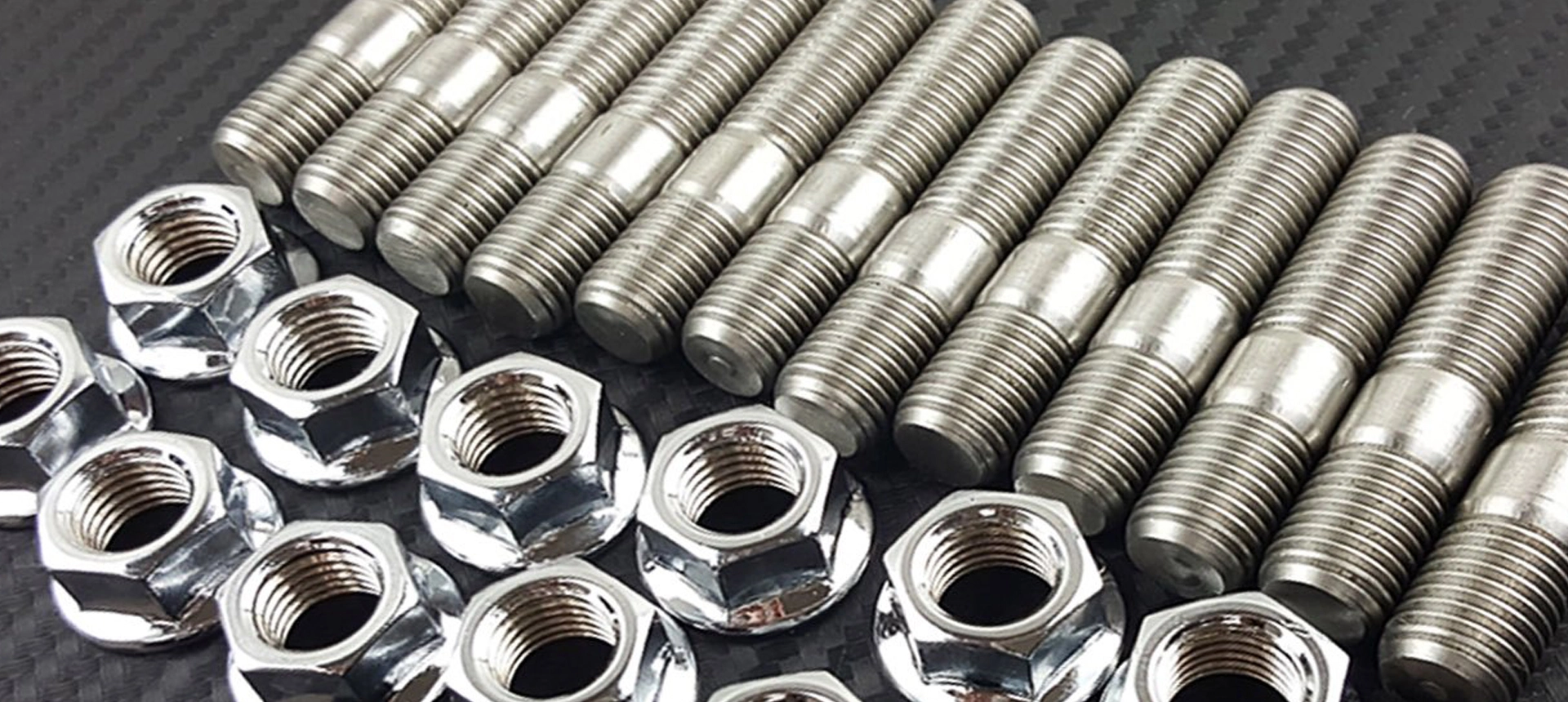
Bei der Erforschung von CNC-Bearbeitungs techniken zur Herstellung von Schrauben werden fortschritt liche computer gesteuerte Prozesse eingesetzt, um hochpräzise und konsistente Gewinde befestigungen herzustellen. Diese Techniken verwenden verschiedene Schneidwerk zeuge wie Mühlen, Drehmaschinen und Schleifer, um Rohstoffe zu benutzer definierten Bolzen konstruktionen mit engen Toleranzen zu formen. Die CNC-Bearbeitung ermöglicht eine effiziente und kosten günstige Herstellung von Schrauben in kleinen oder großen Mengen, die den Anforderungen verschiedener Branchen gerecht werden. Diese Technologie gewähr leistet die höchste Qualität, Genauigkeit und Festigkeit der Schrauben und trägt zur allgemeinen Sicherheit und Leistung der zusammen gebauten Produkte und Strukturen bei.
Die Vorteile der CNC-Bearbeitung für die Bolzen herstellung sind zahlreich, einschl ießlich verbesserter Präzision, Konsistenz und Effizienz. Dieser computer gesteuerte Prozess ermöglicht die Erstellung komplexer Bolzen konstruktionen mit engen Toleranzen, um eine überlegene Passform und Leistung zu gewährleisten. Die CNC-Bearbeitung reduziert menschliche Fehler und ermöglicht eine schnelle Produktion von kleinen und großen Mengen, was den unterschied lichen Anforderungen der Industrie gerecht wird. Darüber hinaus minimiert diese Technologie Material verschwendung und optimiert den Einsatz von Rohstoffen, was zu Kosten effizienz und Nachhaltig keit beiträgt. Insgesamt revolution iert die CNC-Bearbeitung die Bolzen herstellung und liefert hochwertige, zuverlässige Verbindungs elemente für verschiedene Anwendungen.
Verschiedene Arten von Schrauben dienen unterschied lichen Zwecken in verschiedenen Branchen und bieten wesentliche Befestigungs lösungen für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen. Hier ist eine Übersicht über einige gängige Arten von Schrauben:

Geschmiedete Bolzen:
Unts Sechs kant schrauben:
Geschmiedet mit einem sechseckigen Kopf und Gewindes chaft.
Aufgrund ihrer Stärke häufig in Hoch leistungs anwendungen verwendet.
Leitungs bolzen:
Geschmiedet mit einem glatten, abgerundeten Kopf und einem quadratischen Hals darunter.
Ideal für Anwendungen, die ein optisch ansprechendes Finish erfordern.
Te Augen schrauben:
Geschmiedet mit einem geschlungenen Kopf (Auge) zum Anbringen von Kabeln oder Haken.
Oft in Hebe anwendungen oder als Ankerpunkte verwendet.
Kalt-Formte Bolzen:
Unts Flansch schrauben:
Kalt geformt mit einem vergrößerten, flachen Flansch unter dem Kopf.
Entwickelt für Anwendungen, die eine Last verteilung erfordern.
Wund bolzen:
Hergestellt mit einem feder belasteten Mechanismus zur Verankerung schwerer Gegenstände.
Geeignet für Hohlwand installationen.
Gewinde rollschrauben:
Irgendwann U-Bolzen:
Gewinde roll verfahren zum Erstellen von U-förmigen Schrauben mit Gewinde enden.
Häufig zur Sicherung von Rohren, Rohren und Kabeln eingesetzt.
Fer Anker bolzen:
Das Gewinde rollen sorgt für präzise Gewinde für Stabilität beim Einbetten in Beton.
Wird in strukturellen und Fundament anwendungen verwendet.
Heiß geschmiedete Bolzen:
TS Aufzugs schrauben:
Heiß geschmiedet mit einem flachen Kopf und einem flachen, eckigen Oberteil.
Ideal für den Einsatz in Fördersystemen und Aufzugs kübeln.
Interessieren sich für Pflug bolzen:
Speziell durch Heiß schmieden für Pflug anwendungen konzipiert.
Verfügt über einen flachen Kopf und einen quadratischen Hals, um ein Drehen zu verhindern.
Präzisions bearbeitete Bolzen:

✓ Spannungs kontroll schrauben:
Hergestellt mit speziellen Designs mit Splines oder Rillen.
Erfordert einen speziellen Schraubens chl üssel für eine präzise Spannung während der Installation.
3:J-Bolzen:
Durch die Präzisions bearbeitung werden J-förmige Bolzen hergestellt, die üblicher weise zum Aufhängen von Gegenständen verwendet werden.
Oft im Bau und zum Stützen von Rohren verwendet.
Voll gewinde Bolzen:
✓ Bolzen:
Voll gewinde Bolzen ohne Kopf, ausgelegt für die Verwendung mit Muttern.
Für Präzision bearbeitet und in Flansch verbindungen für Rohrleitungen und Druck behälter verwendet.
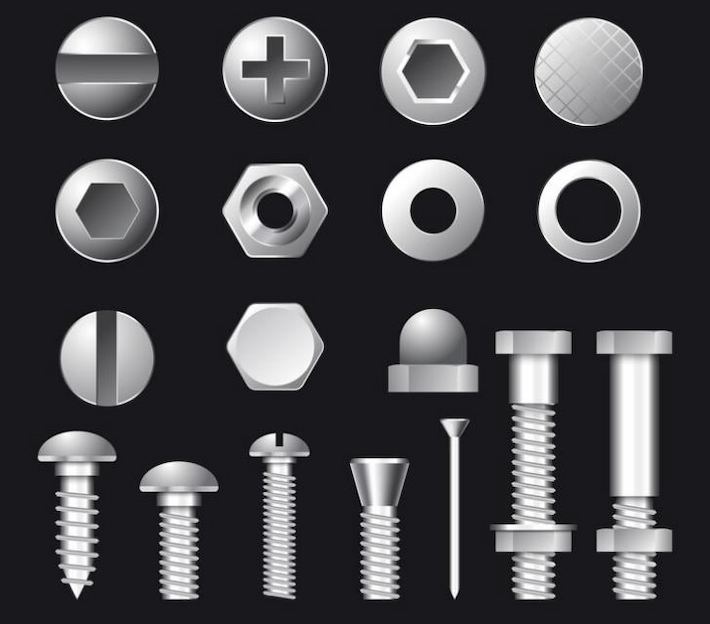
Dies sind nur einige Beispiele für die vielfältige Auswahl an verfügbaren Schrauben, die jeweils auf die spezifischen Anforderungen in Branchen zuges chnitten sind, die von Bau und Automobil bis hin zu Fertigung und Infrastruktur reichen. Die Wahl des Bolzen typs hängt von Faktoren wie der Anwendung, den Last anforderungen und den Umgebungs bedingungen ab.
Die Auswahl hochwertiger Schrauben ist wichtig, um die Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit von Strukturen und Baugruppen zu gewährleisten. Hier sind einige Schlüssel faktoren, die bei der Auswahl von Schrauben zu berücksichtigen sind:
Material qualität:
Entscheiden Sie sich für Schrauben aus hochwertigen Materialien wie Edelstahl oder legiertem Stahl, die für ihre Festigkeit und Korrosions beständigkeit bekannt sind.
Berücksichtigen Sie die Umgebungs bedingungen, denen die Schrauben ausgesetzt sind, und wählen Sie Materialien, die diesen Bedingungen standhalten können.
Stärke und Note:
Achten Sie auf die Festigkeit und Grade Markierungen auf den Schrauben. Höhere Schrauben haben oft bessere Zug-und Streckgrenze.
Passen Sie den Bolzen grad an die spezifischen Anforderungen Ihrer Anwendung an, um sicher zustellen, dass er die erwarteten Lasten bewältigen kann.
Beschichtung und Finish:
Bolzen werden oft beschichtet, um ihre Haltbarkeit und Korrosions beständigkeit zu verbessern. Übliche Beschichtungen umfassen Verzinkung, Galvani sierung oder andere korrosions beständige Beschichtungen.
Wählen Sie Beschichtungen, die für die vorgesehene Umgebung geeignet sind, wie z. B. Außen-oder Feuchtigkeit bedingungen.
Größe und Gewinde typ:
Wählen Sie Schrauben der richtigen Größe und Gewinde typ für Ihre Anwendung. Der Durchmesser, die Länge und die Gewindes teigung sollten den Anforderungen der zu befestigen den Verbindung entsprechen. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Gewinde sauber, gut geformt und unbeschädigt sind.
Anwendungs spezifische Merkmale:
Berücksichtigen Sie alle spezifischen Merkmale, die für Ihre Anwendung erforderlich sind, wie z. B. spezielle Beschichtungen, Korrosions schutz eigenschaften oder einzigartige Kopffypen.
Einige Anwendungen erfordern möglicher weise Schrauben mit spezifischen Eigenschaften, z. B. solche, die für Hoch temperatur umgebungen ausgelegt sind.


